Mental health plays a significant role in both the well-being of individual employees and the overall success of an organization. When mental health is prioritized, it can lead to a positive and productive work environment. However, when mental health is neglected, it can have profound negative effects on both employees and employers alike. Here’s a breakdown of how mental health impacts both groups:
1. Impact on Employees
- Productivity and Job Performance:
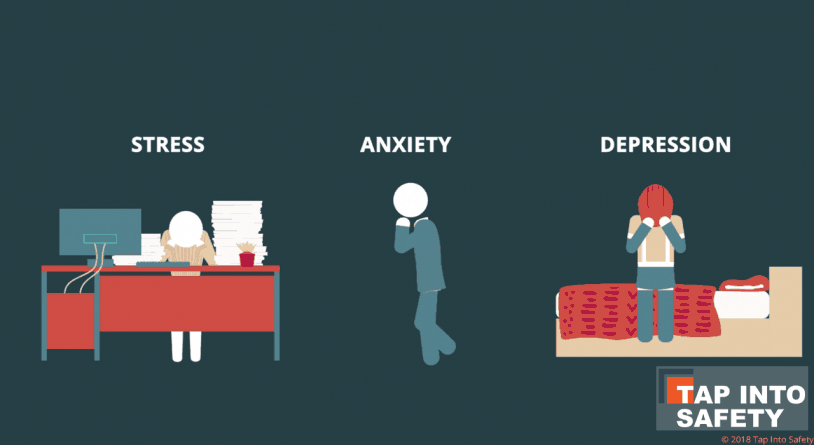
Mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, or stress can significantly impair an employee’s ability to perform at their best. When employees are dealing with mental health issues, they often experience difficulty focusing, staying motivated, or completing tasks effectively. This can lead to decreased productivity, mistakes, and lower quality of work. Even high-performing employees may struggle to maintain their usual levels of output during difficult times. - Absenteeism and Presenteeism:
Mental health struggles can lead to both absenteeism and presenteeism. Absenteeism refers to employees taking time off work because they are unable to manage their mental health, leading to missed workdays. Presenteeism, on the other hand, occurs when employees show up to work but are not fully functioning due to mental health challenges. They may be physically present, but they are less engaged, less efficient, and may not be producing their best work. Both absenteeism and presenteeism reduce overall workplace efficiency and can be costly to businesses. - Burnout and Emotional Exhaustion:
Chronic stress and the pressure of balancing work and personal responsibilities can lead to burnout. Employees who experience burnout feel emotionally drained, overwhelmed, and disconnected from their work. They may have trouble finding motivation and experience a lack of fulfillment in their roles. Burnout can cause employees to feel disengaged, which can lead to dissatisfaction and a desire to leave the company. - Physical Health Impact:
Mental health problems often manifest physically. Stress and anxiety can lead to physical symptoms like headaches, fatigue, digestive issues, or sleep problems. Over time, these physical symptoms can worsen, leading to more serious health issues like heart disease or hypertension. Employees may take more sick days, suffer from long-term health problems, or struggle to focus on their jobs due to physical discomfort. - Job Satisfaction and Well-Being:
Mental health challenges can make employees feel unsupported, undervalued, or isolated. If a workplace doesn’t provide mental health resources or create a supportive environment, employees may feel disengaged or unappreciated. This can lead to a decrease in job satisfaction, resulting in higher turnover rates, decreased morale, and a toxic workplace culture. Employees who feel mentally well are more likely to be happy at work and feel more connected to their colleagues and the organization.
2. Impact on Employers
- Decreased Productivity and Efficiency:
Employers rely on their employees to contribute to the success of the business. When employees are struggling with mental health challenges, their ability to perform tasks, meet deadlines, and deliver high-quality work can be compromised. This impacts the overall productivity of the team and can slow down the pace of business operations. It may also lead to delays in project completion and hinder innovation or problem-solving. - Increased Costs:
Mental health issues can lead to a range of financial costs for employers. Direct costs include healthcare expenses for treating mental health conditions, while indirect costs include reduced productivity, absenteeism, presenteeism, and employee turnover. According to various studies, organizations that do not address mental health issues effectively may experience higher healthcare costs and increased worker compensation claims. For example, stress-related illnesses can contribute to long-term medical leave or workers’ compensation claims. - Employee Turnover and Recruitment Challenges:
Employees who are mentally unwell and feel unsupported may leave the company in search of a better work environment. High turnover rates can be costly for employers, who must spend time and resources on recruiting, hiring, and training new staff. Additionally, a lack of mental health support in the workplace can damage an organization’s reputation, making it harder to attract and retain top talent. - Workplace Culture and Morale:
The overall culture and morale of a workplace are heavily influenced by how mental health is addressed. If mental health issues are ignored or stigmatized, it can create a toxic work environment. Employees may feel reluctant to speak up about their struggles or seek help, which leads to a sense of isolation and disengagement. On the other hand, a workplace that supports mental health creates a positive and collaborative environment where employees feel safe, valued, and respected. A supportive culture helps employees build strong relationships and work cohesively toward common goals. - Legal and Compliance Issues:
In many countries, employers are legally obligated to ensure the well-being of their employees, including addressing mental health concerns. Failure to provide a mentally healthy work environment can lead to legal issues, including lawsuits related to workplace discrimination, harassment, or failure to accommodate employees with mental health conditions. Employers may also face regulatory scrutiny or penalties if they do not comply with laws that protect employee mental health and safety. - Leadership and Company Success:
Employers and leaders who prioritize mental health can have a lasting impact on the overall success of the organization. Leaders who show empathy, create a supportive work environment, and encourage open communication foster a culture of trust and loyalty. When employees feel supported in their mental health, they are more likely to stay motivated, contribute their best work, and be engaged with the company’s goals. This positively impacts business outcomes, from productivity and profitability to brand reputation and long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, mental health affects both employees and employers in profound ways. When employees struggle with mental health issues, it impacts their productivity, job satisfaction, and well-being. On the other hand, employers face challenges related to increased costs, absenteeism, presenteeism, and higher turnover. Creating a workplace culture that supports mental health is not just a moral obligation — it’s a business imperative. By prioritizing mental health in the workplace, employers can reduce costs, improve productivity, and foster a more engaged and loyal workforce, benefiting both employees and the organization as a whole.
This breakdown explains the wide-reaching impact of mental health in the workplace, covering both employees’ personal experiences and the broader organizational implications. If you’d like any further details or examples, feel free to ask!